Category: Earth Science
When Whirlwinds Meet Hot Lava: Lava Devils!
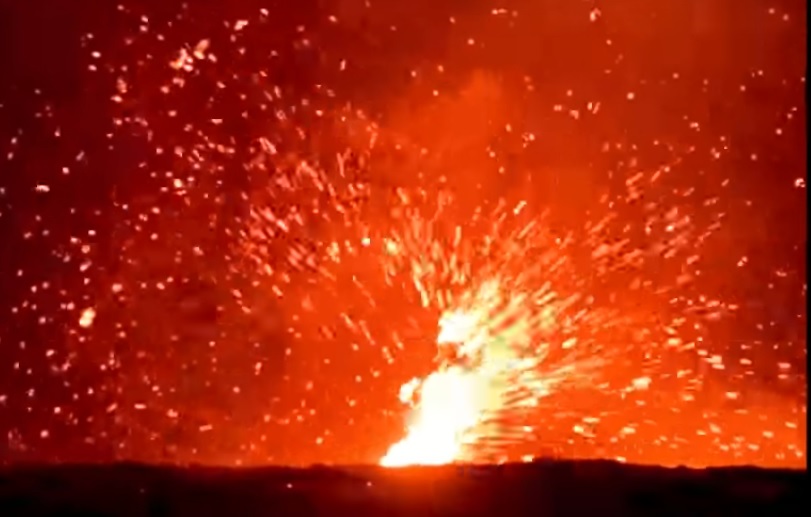

There are so many things to see while watching a livestream of a volcanic eruption. Lava fountains, spatter cones being built up and falling down, turbulence in lava flows… and lava devils?!
Yes, indeed! Keep your focus on the left in the video below, and you’ll see molten lava sucked up and flung about by a vigorous little whirlwind during Kilauea’s latest summit eruption: (more…)
42 for Loowit’s 42nd vol. 6: Beauty in Destruction
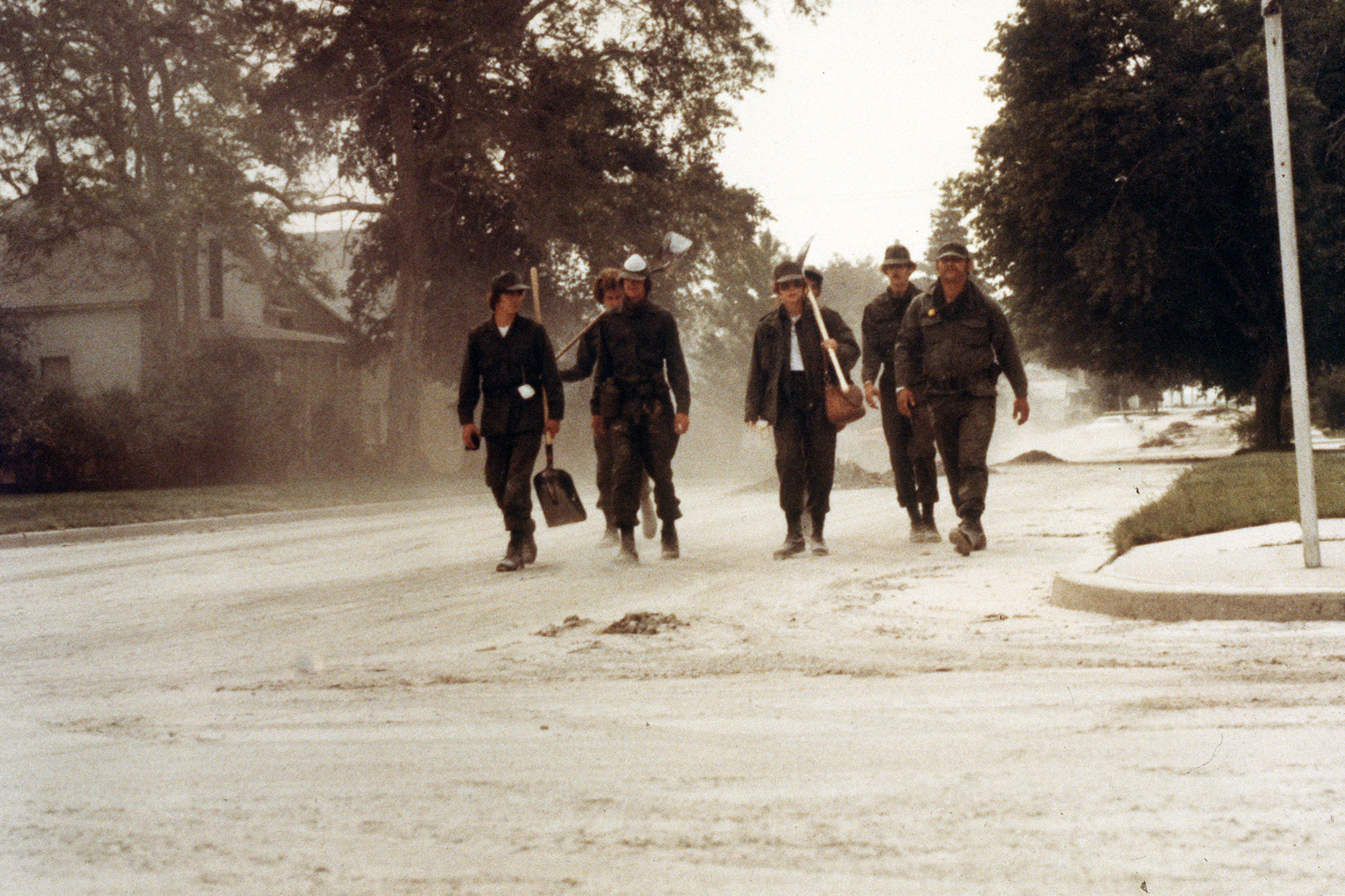

Volcanoes leave one heck of a mess to clean up when they explode near civilization. It’s not pretty, although as you can see above, it sometimes looks pretty metal.
While Washington State called out the National Guard and folks figured out how to cope with the copious ash, volcanologists picked through the ruins of a once-verdant forest, measuring various volcanic deposits and learning all they could from them. At first, it was shocking. But once you started adjusting to the change, you could start seeing the beauty in the devastation.
Look at the channel carved through the debris avalanche here: you can see gorgeous reds in the gray where hydrothermally altered rock from the former summit mixed with the more prosaic grays of younger material. The iron-stained creek flowing through added more color to the moonscape. It was alien and strangely pretty. (more…)
The Standing of the Stones Spring ’22 Edition

(A version of this post first appeared on Patreon. To get early access, plus nifty extras, all while supporting Rosetta Stones, please click here.)
Yeah, it has been a long time since I wrote something substantial, hasn’t it? Even Women’s History Month passed without a peep. Both work and my poor teeth exploded, so it’s been a few months of ending up too drained to word properly while I take care of those matters. Thank you so much for sticking with me regardless. It’s about to get good and earth sciency around here.
I haven’t been completely idle: I’ve been researching Marguerite Thomas Williams, the first African American to earn a PhD in geology. Dozens of articles are out there about her. Precisely none contain any of her words. They list off the same few facts, mostly, which tell us some important and interesting things about her, but don’t give her a living memory. She feels remote, removed, like we’re viewing a damaged newsreel from the back of a theater with a moth-eaten screen and a failing projector. Some of the facts given are there to try to illustrate how unique she was, but they’re wrong: she wasn’t born in the Reconstruction era, in fact was nearly twenty years too late. Even the photo many use to portray her isn’t actually her.
The Year in Volcanoes at Rosetta Stones
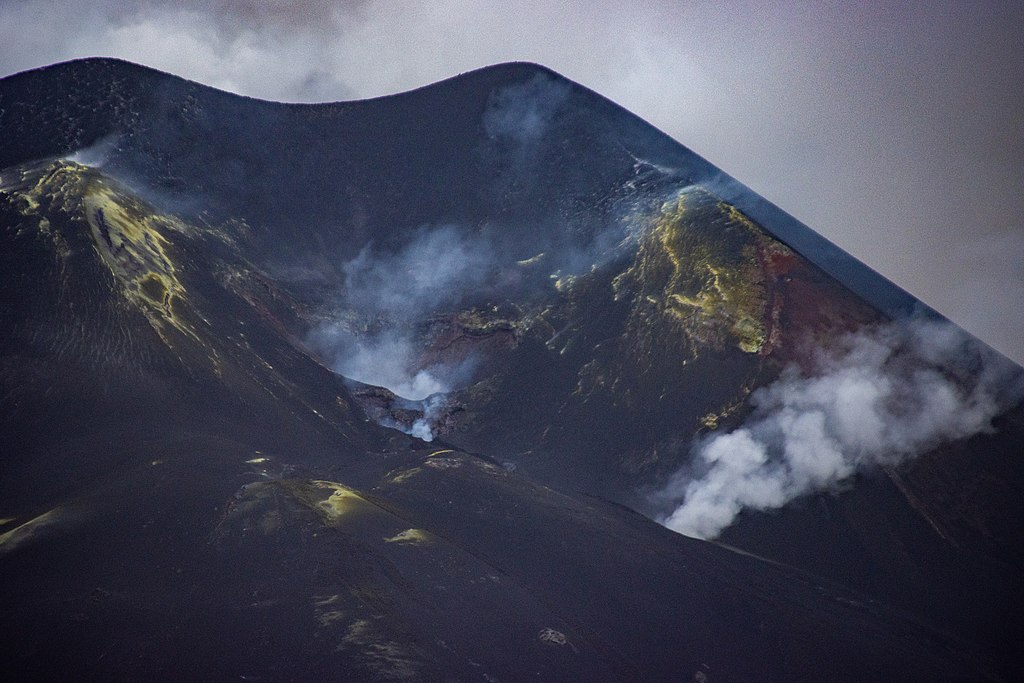

2021 was an excellent year for eruptions that were fascinating to watch and not terribly dangerous to humans! Let’s look back on the eruptions we covered, and see where they are now, and what might be in store for 2022.
Kilauea, United States
Tūtū Pele has celebrated the last couple of New Years with sweet summit eruptions. From late December 2021 through most of May of 2021, we were treated to a spectacular end to the water lake in the crater and entertained by the dancing islands of the new lava lake. Pele took the summer off before abruptly returning on September 29th. She’s been putting on a crater lava show ever since, with just a few breaks, including a pause over Christmas. By the new year, she was back in action and put on a lovely show over the holiday.
Since Pelee’s only taken one year off since the 1980s, I’m expecting this year to include some gorgeous lava action from her current home. And stay tuned to see if she does any remodeling at Mauna Loa!
Geldingadalir (Fagradalsfjall), Iceland (more…)
Why La Palma is Like This vol. I: The Seamount that Soared
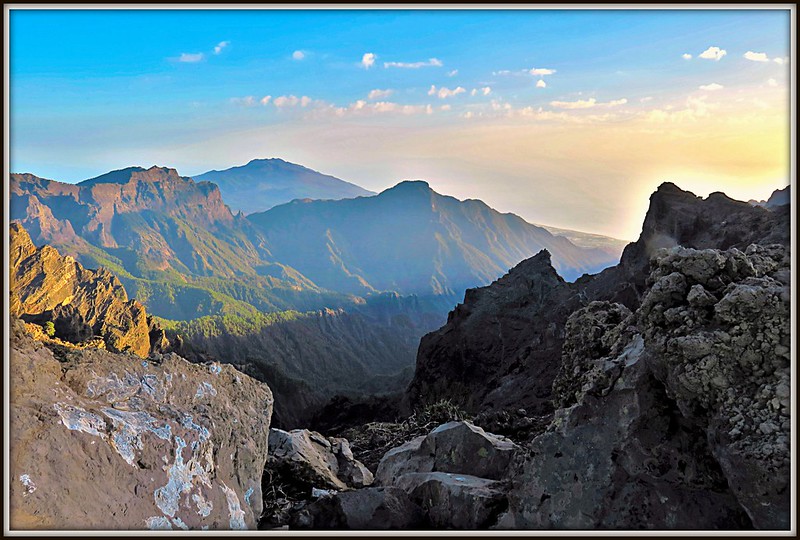

This post first appeared on Patreon. To get early access, plus exclusive extras, please visit my Patreon page.
Now that we’ve got the geologic context of the Canary Islands as a whole figured out, it’s time to zero in on La Palma. How did she get here? Why are all the recent eruptions happening only on one half of her? What might be in store for the future? Does the fact that the most recent eruption is the longest and most voluminous of her entire recorded history mean the island is doomed? And is her active volcanic ridge, Cumbre Vieja, going to fall into the ocean and wipe out the East Coast of North America?
(I won’t keep you in suspense on that last one: the answer is almost certainly a resounding no. So while we’ll talk a bit about former collapses that have shaped the island, we won’t be spending any time on the megatsunami theory. Sorry not sorry.)
A Brief History of La Palma
La Palma is the second-youngest Canary island, and is still growing. She is, in fact, the most vigorously volcanic of the Canary Islands, boasting the most eruptions on record since the Spanish settlers arrived. And that’s just the last 500-ish years of her history: she’s actually about four million years old, if you count from her birth as a bouncing baby seamount. Nearly all of those years involve very hot rocks. (more…)
The Blanco Fault Zone Rides Again
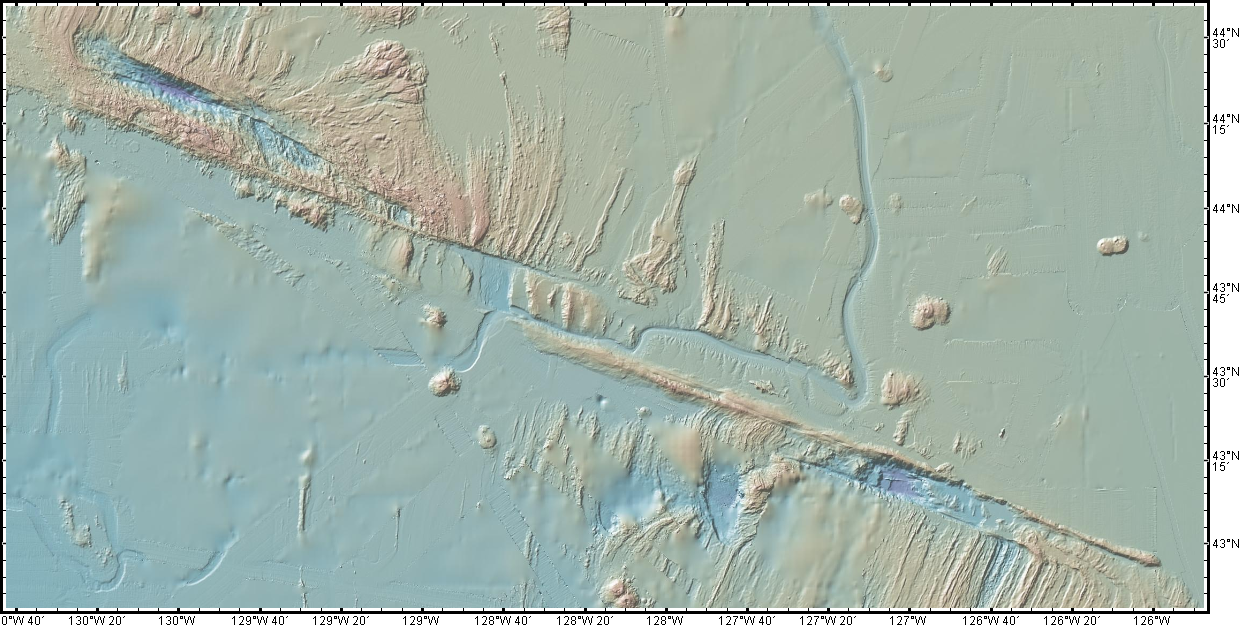
Do we have to do this again so soon? Really? Oh, geez.

Must we really, CNN? Credit: Dana Hunter
I’m not going to link that article, because while it does quote seismologist Harold Tobin up front basically saying nothing to see here, folks, everything’s normal on the Blanco Fault Zone, it also tries to scaremonger. And I’m so over the scaremongering.
Listen. This is the Blanco Fault Zone. Earthquake swarms with many temblors of this magnitude are its specialty. It means absolutely nothing for the mainland. Zip. Zilch. Nada. Read this very good article on Oregon Public Broadcasting, which laid out the facts in beautiful form.
And no, this has utterly nothing to do with submarine volcanoes. No, not even Axial seamount. Dr. Jackie Caplan-Auerbach wrote an entire post explaining how much it’s not that:
There have been a lot of questions about the recent Blanco tranform activity, including whether these are related to volcanic activity in general, and Axial Seamount in specific. The short answer is no, these are definitively not volcanic quakes, but more detail follows.
First, the Blanco Transform fault is the most active fault in the Pacific NW, with very frequent quakes >M5. We can tell that these are normal Blanco faults by their location, by the way they fail (these are strike-slip earthquakes, consistent with the fault’s normal behavior, and happily, the type least likely to generate tsunamis).There is no volcanism associated with transform faults. The nearest frequently active volcano (and the one people most often ask about) is Axial seamount, which is ~300 km from the activity we are seeing on the Blanco this week. This is much too far apart for these features to be associated with one another.
And I swear we all have to do this every dang time.
For anyone who’s been worried that this is the harbinger of something geologically awful in the Pacific Northwest, please be assured that it is not. This is absolutely business as usual on the Blanco Fault Zone. This is what it does. It’s not going to trigger the Cascadia megatsunami. It’s not even going to cause any minor inconveniences to the mainland. Volcanoes aren’t going to be triggered. Literally the only way it’s going to become an issue is if we decide to build a seafloor city right on top of it. Which, knowing humans, someday we will definitely do.
Just a hair over two years ago, my Scientific American article explained why the Blanco should be considered a fun rather than fearsome fault zone. I shall now reproduce that article here, because literally nothing has changed except the date. Please bookmark this to reference whenever someone starts freaking out over the Blanco’s latest antics. It’s all chill, folks. Just enjoy it’s little productions! Because they’re actually entertaining and informative from an earth science perspective, just the way we like our geology. (more…)
Standing of the Stones: Island Volcanoes Abounding Edition

Hello and welcome to a new, semi-weekly feature in which I’ll share snippets of earth science news, cool things I’ve stumbled across, pretty pictures, status reports on upcoming articles, and whatever else seems interesting.
La Palma: Still on Fire
This has been one of the longest eruptions in La Palma’s recorded history, and is posed to be the longest, if it keeps going. Some of the recent lava fountains have exceeded 1,600 feet (500m) in height. The person who runs the GeologyHub channel has discovered a pattern in the data that suggests something interesting (and ominous to the locals) about the relationship between deep earthquakes and eruption activity on the island.
Can you believe where some of that ash ended up?!
It looks like the eruption may break some records. Interesting times indeed.
Why Is La Palma Like This?
Iceland from the West to the South: A Meh Guide With Some Eye-Popping Mistakes

(This post first appeared on Patreon. To get early access, plus nifty extras, all while supporting Rosetta Stones, please click here.)
So of course with all of the Iceland Volcano excitement, I had to run out and buy a bunch of books on Icelandic geology. It’s actually not super easy to find affordable ones in English. So I was very pleased to find one published by Springer for a good price: Iceland from the West to the South by Wolfgang Fraedrich. Springer is all about science written by scientists. I was stoked.
I have now read it, and…I’m considerably less stoked.
Ghostly Geology

Halloween is here! This is my favorite part of fall: costumes, spooky stuff, decorating in black not only allowed but encouraged…. This is the holiday I was born for.
And I have some geology made for the holiday! This year, the theme is ghosts, and we’re going to visit some very ghostly geology and paleontology indeed.
1. Ghost Shrimp Haunts Ichnologist

This is a different kind of ghost shrimp than the ones under discussion, but it is metal enough for Halloween, so we’re rolling with it. Credit:
Freddie Alequin (CC BY-SA 2.0)
Paleontology isn’t just about bones and preserved bodies: a branch of it, ichnology*, also looks at the things those bodies left behind, like fossilized trails, tracks, nests, burrows, borings, excavations, and even the divots left by pee. In this post, my favorite ichnologist, Tony Martin, talks about a very unusual trace he found that would be even more exciting to find in the fossil record.
Life Traces of the Georgia Coast: Ghost Shrimp Whisperer
Geologists love ghost shrimp, too, because of how their burrows are so numerous, fossilize easily, and are sensitive shoreline indicators. I wrote about this before with regard to how geologists in the 1960s were able to map ancient barrier islands of the Georgia coastal plain by looking for trace fossils of these burrows. Since then, geologists and paleontologists have identified and applied these sorts of trace fossils worldwide, and in rocks from the Permian Period to the Pleistocene Epoch.
I could prattle on about ghost shrimp and their ichnological incredibleness for the rest of the year, but will spare you of that, gentle reader, and instead will get to the point of this post. Just when I thought I’d learned nearly everything I needed to know about ghost-shrimp ichnology, one shrimp decided I needed to have my eyes opened to some traces I had never seen them make before just a few months ago.
*Not to be confused with ichthyology, which has to do with fishies. It’ll help to remember that ikhnos means “track” or “trace” in Greek, while ikhthus means “fish.”
2. Ghosts of Minerals Past (more…)
Why the Canary Islands are Like This
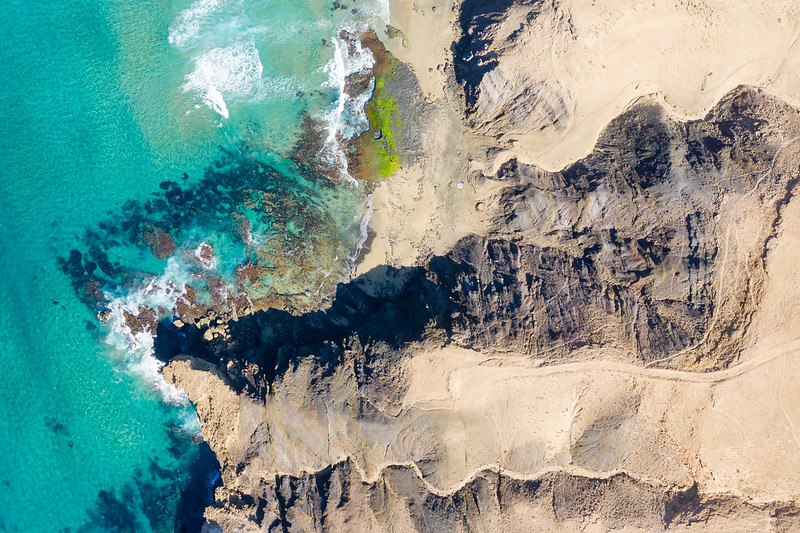

This post first appeared on Patreon. To get early access, plus exclusive extras, please visit my Patreon page.
The current eruption on La Palma in the Canary Islands is now over a month old. Already the island’s largest in a hundred years, it’s giving no signs of stopping just yet. Volcano lovers have thrilled to its spectacular Strombolian explosions. Residents have endured disruption, displacement, and loss of homes and livelihoods. Dogs trapped by lava flows had to be fed by drone before they were taken to safety in a daring and mysterious rescue. Living with a live volcano is far from easy and seldom safe.
Plenty of news agencies, vloggers, and blogs are keeping us up to date on the progress of the current eruption. I’m going to take us deep into the past, on a journey into the island’s origins and evolution. We’re going to see the slow, steady pas de deux between a mantle plume and the plate above it. We’ll watch underwater volcanoes go subaerial, building new land, and see catastrophic collapses tear their confections down. We’ll learn the life stages of a Canary Island, and by the end, we’ll know the broad outlines of La Palma’s destiny.
In the end, we’ll see that this current eruption is as much an act of creation as it is destruction.

Mirador de La Tarta, Tenerife. Yes, it’s literally called a cake! The white layer is pumice, the black layers are basaltic scoria, and the reddish-brown layers are oxidized basaltic tephra. Credit: H. Zell (CC BY-SA 3.0)
