Tag: natural disaster
42 for Loowit’s 42nd vol. 3: Ominous April

For the people who lived and worked on the flanks of Loowit (Mount St. Helens), her awakening was both curse and blessing. Living with a restless stratovolcano isn’t safe nor comfortable. But the tourism it draws is great for the local economy. Locals leaned in, creating funny hats and shirts, renaming menu items, and finding other creative ways to capitalize on her activity.
For the scientists who flocked to her, it was the chance of a lifetime.

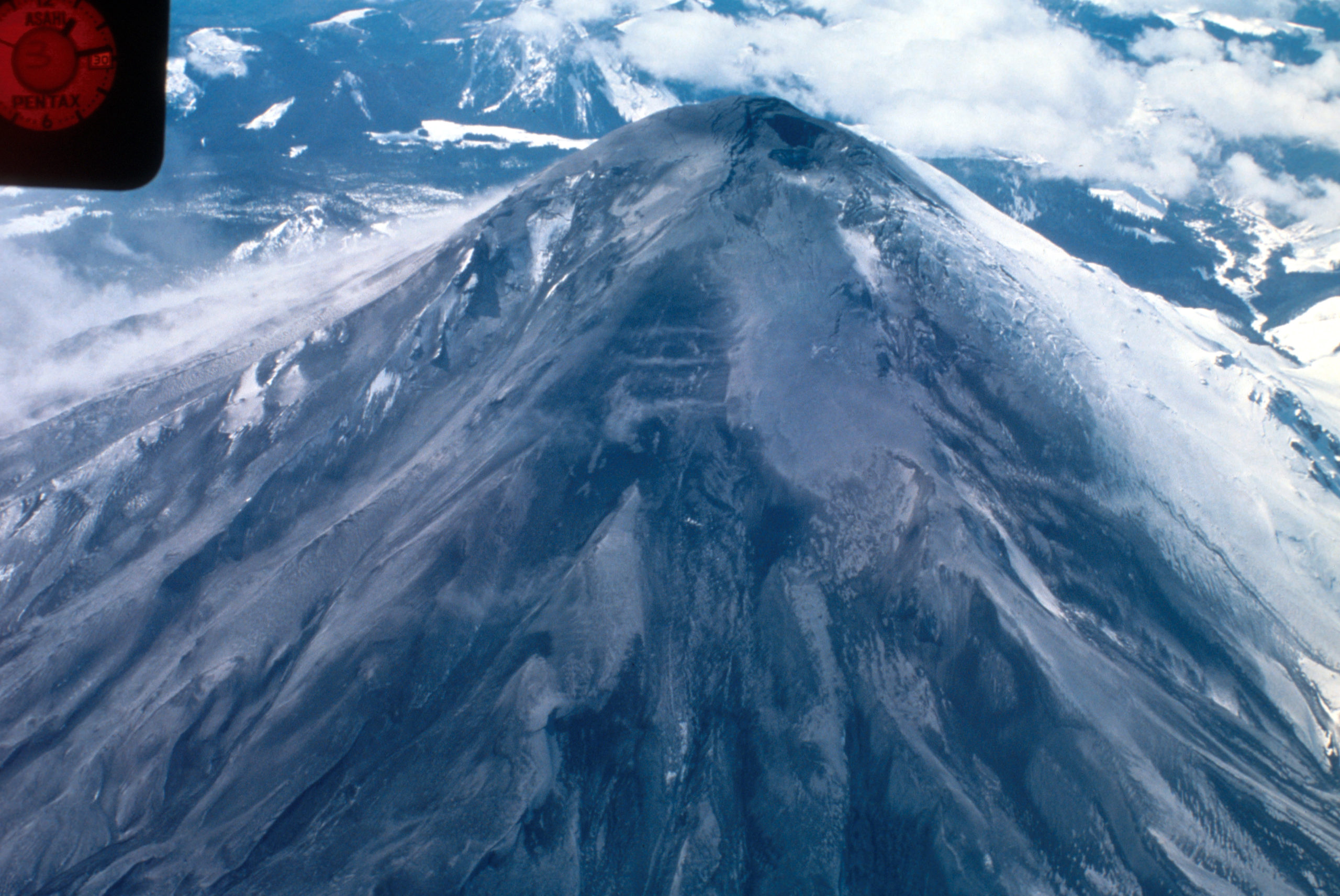
Aerial view of Mount St. Helens and drifting plume, from northwest. Photo taken from U.S. Forest Service observer plane at 12:32 p.m. Skamania County, Washington. April 4, 1980. Caption and image credit: USGS
Volcanologists flocked to her slopes, installing equipment, taking measurements and photos, and flying over the summit as steam and ash spurted into the sky. They’d seldom had a chance to study an actively erupting composite cone so conveniently close to highways and large cities. Loowit was wonderfully accessible, and easy to observe, even in the Pacific Northwest’s capricious early spring weather. (more…)
42 For Loowit’s 42nd vol. 2: March Awakening

There’s this old saying about March: “In like a lamb, out like a lion.” This turned out to be very true in Loowit’s case as the 1980s began.
After over a century of peaceful slumber, Loowit (Mount St. Helens) began to wake. Seismic activity is nothing new around volcanoes, but this swarm was intense enough to shake the snow from her summit.

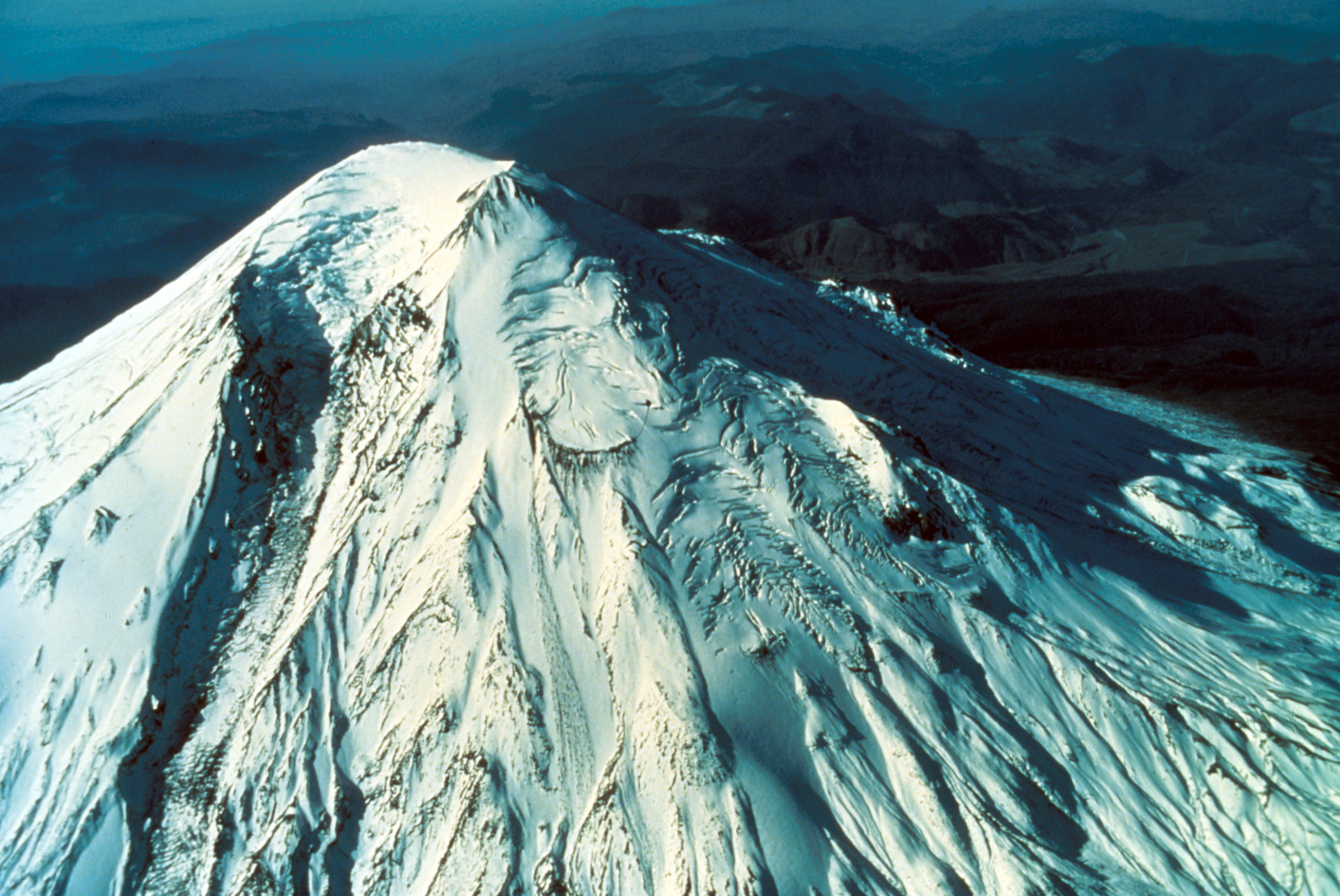
North side of Mount St. Helens, Washington, as of 24 March 1980. Numerous snow avalanche fracture scarps may be related to continued earthquake shaking. No signs of volcanic activity are evident. Caption and image credit: USGS
She still looked lovely and serene, but as March waned, signs became increasingly clear that magma was on the move in a serious way. (more…)
42 for Loowit’s 42nd vol. 1: Pre-1980 Majesty

What’s the answer to life, the Universe, and how many years it’s been since Loowit (Mount St. Helens) erupted? Why, 42, of course! We’ve plundered the archives of the United States Geological Survey and the US Forest Service for 42 of the best historical photos, plus bonus featured images.
Grab your towels and join me on an epic journey back to the 20th Century, in those years when plate tectonics was still in its infancy, volcanology was still young, and Loowit had yet to stir.
The Year in Volcanoes at Rosetta Stones

2021 was an excellent year for eruptions that were fascinating to watch and not terribly dangerous to humans! Let’s look back on the eruptions we covered, and see where they are now, and what might be in store for 2022.
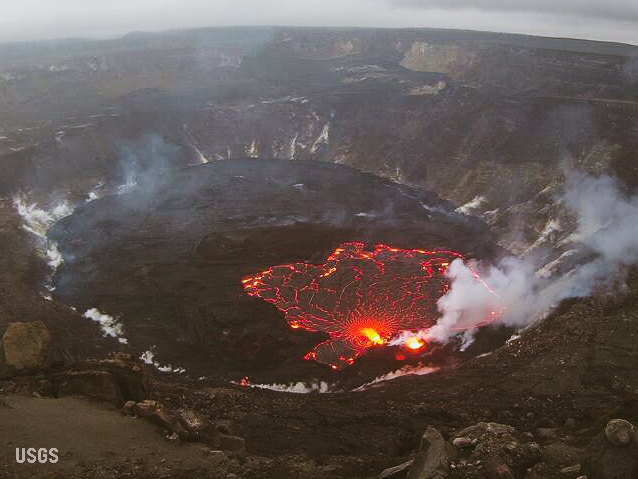
Kilauea, United States
Tūtū Pele has celebrated the last couple of New Years with sweet summit eruptions. From late December 2021 through most of May of 2021, we were treated to a spectacular end to the water lake in the crater and entertained by the dancing islands of the new lava lake. Pele took the summer off before abruptly returning on September 29th. She’s been putting on a crater lava show ever since, with just a few breaks, including a pause over Christmas. By the new year, she was back in action and put on a lovely show over the holiday.
Since Pelee’s only taken one year off since the 1980s, I’m expecting this year to include some gorgeous lava action from her current home. And stay tuned to see if she does any remodeling at Mauna Loa!
Geldingadalir (Fagradalsfjall), Iceland (more…)
The Blanco Fault Zone Rides Again
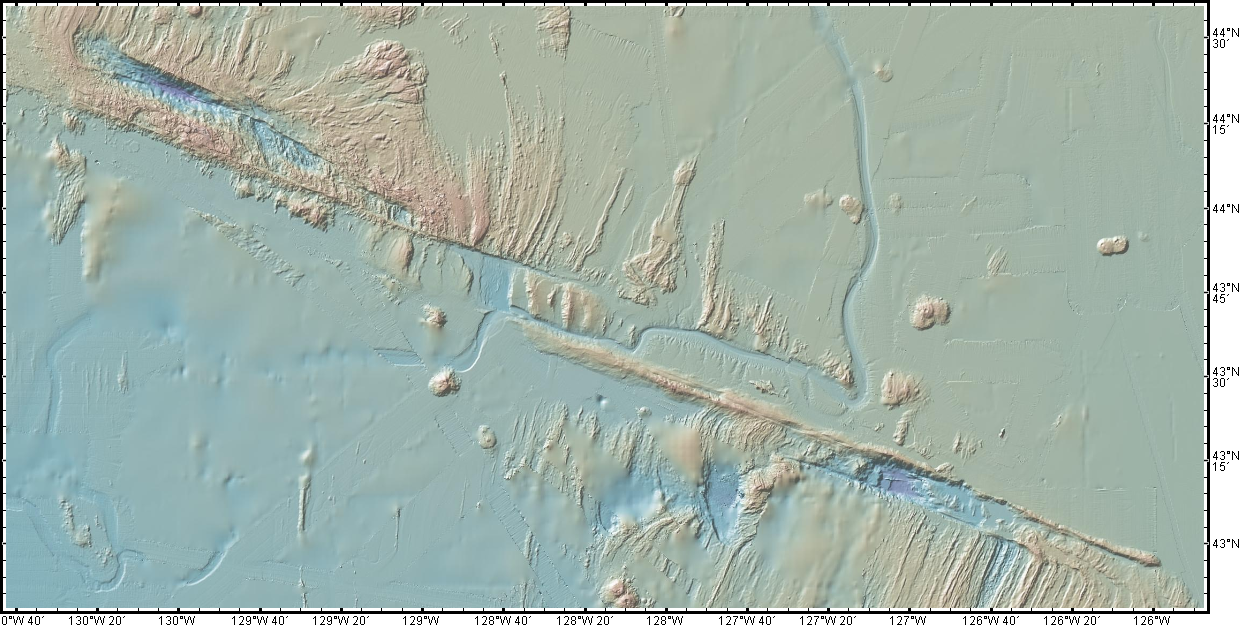
Do we have to do this again so soon? Really? Oh, geez.

Must we really, CNN? Credit: Dana Hunter
I’m not going to link that article, because while it does quote seismologist Harold Tobin up front basically saying nothing to see here, folks, everything’s normal on the Blanco Fault Zone, it also tries to scaremonger. And I’m so over the scaremongering.
Listen. This is the Blanco Fault Zone. Earthquake swarms with many temblors of this magnitude are its specialty. It means absolutely nothing for the mainland. Zip. Zilch. Nada. Read this very good article on Oregon Public Broadcasting, which laid out the facts in beautiful form.
And no, this has utterly nothing to do with submarine volcanoes. No, not even Axial seamount. Dr. Jackie Caplan-Auerbach wrote an entire post explaining how much it’s not that:
There have been a lot of questions about the recent Blanco tranform activity, including whether these are related to volcanic activity in general, and Axial Seamount in specific. The short answer is no, these are definitively not volcanic quakes, but more detail follows.
First, the Blanco Transform fault is the most active fault in the Pacific NW, with very frequent quakes >M5. We can tell that these are normal Blanco faults by their location, by the way they fail (these are strike-slip earthquakes, consistent with the fault’s normal behavior, and happily, the type least likely to generate tsunamis).There is no volcanism associated with transform faults. The nearest frequently active volcano (and the one people most often ask about) is Axial seamount, which is ~300 km from the activity we are seeing on the Blanco this week. This is much too far apart for these features to be associated with one another.
And I swear we all have to do this every dang time.
For anyone who’s been worried that this is the harbinger of something geologically awful in the Pacific Northwest, please be assured that it is not. This is absolutely business as usual on the Blanco Fault Zone. This is what it does. It’s not going to trigger the Cascadia megatsunami. It’s not even going to cause any minor inconveniences to the mainland. Volcanoes aren’t going to be triggered. Literally the only way it’s going to become an issue is if we decide to build a seafloor city right on top of it. Which, knowing humans, someday we will definitely do.
Just a hair over two years ago, my Scientific American article explained why the Blanco should be considered a fun rather than fearsome fault zone. I shall now reproduce that article here, because literally nothing has changed except the date. Please bookmark this to reference whenever someone starts freaking out over the Blanco’s latest antics. It’s all chill, folks. Just enjoy it’s little productions! Because they’re actually entertaining and informative from an earth science perspective, just the way we like our geology. (more…)
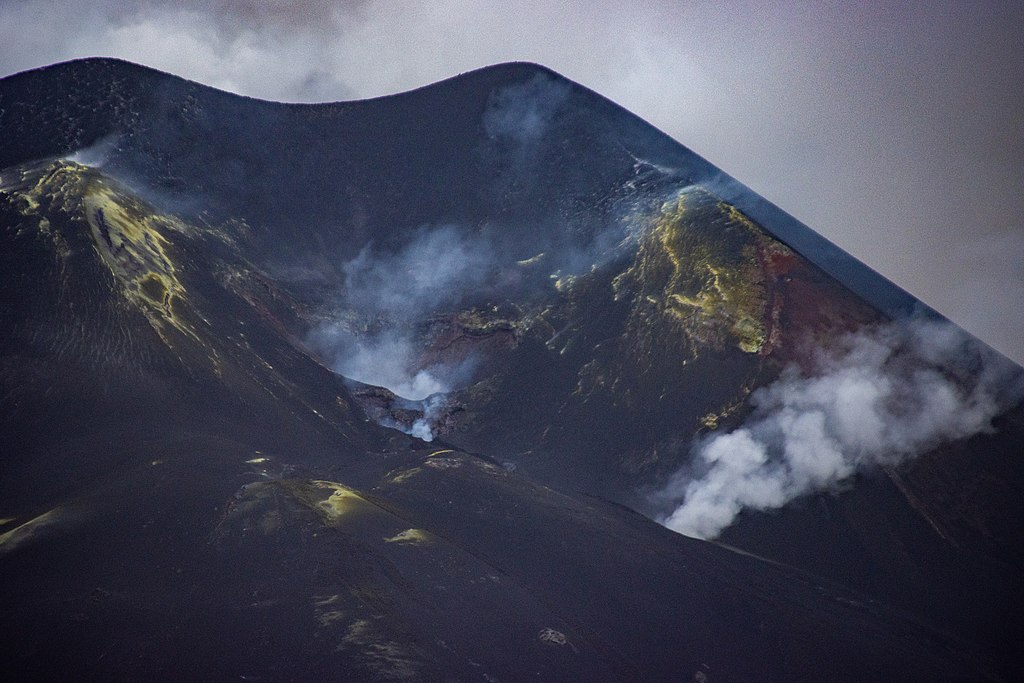
Standing of the Stones: Island Volcanoes Abounding Edition

Hello and welcome to a new, semi-weekly feature in which I’ll share snippets of earth science news, cool things I’ve stumbled across, pretty pictures, status reports on upcoming articles, and whatever else seems interesting.
La Palma: Still on Fire
This has been one of the longest eruptions in La Palma’s recorded history, and is posed to be the longest, if it keeps going. Some of the recent lava fountains have exceeded 1,600 feet (500m) in height. The person who runs the GeologyHub channel has discovered a pattern in the data that suggests something interesting (and ominous to the locals) about the relationship between deep earthquakes and eruption activity on the island.
Can you believe where some of that ash ended up?!
It looks like the eruption may break some records. Interesting times indeed.
Why Is La Palma Like This?
Why the Canary Islands are Like This

This post first appeared on Patreon. To get early access, plus exclusive extras, please visit my Patreon page.
The current eruption on La Palma in the Canary Islands is now over a month old. Already the island’s largest in a hundred years, it’s giving no signs of stopping just yet. Volcano lovers have thrilled to its spectacular Strombolian explosions. Residents have endured disruption, displacement, and loss of homes and livelihoods. Dogs trapped by lava flows had to be fed by drone before they were taken to safety in a daring and mysterious rescue. Living with a live volcano is far from easy and seldom safe.
Plenty of news agencies, vloggers, and blogs are keeping us up to date on the progress of the current eruption. I’m going to take us deep into the past, on a journey into the island’s origins and evolution. We’re going to see the slow, steady pas de deux between a mantle plume and the plate above it. We’ll watch underwater volcanoes go subaerial, building new land, and see catastrophic collapses tear their confections down. We’ll learn the life stages of a Canary Island, and by the end, we’ll know the broad outlines of La Palma’s destiny.
In the end, we’ll see that this current eruption is as much an act of creation as it is destruction.

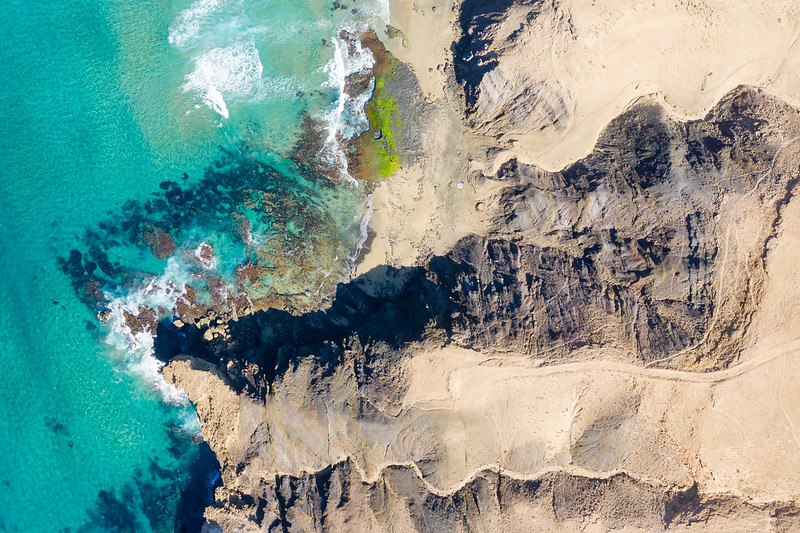
Mirador de La Tarta, Tenerife. Yes, it’s literally called a cake! The white layer is pumice, the black layers are basaltic scoria, and the reddish-brown layers are oxidized basaltic tephra. Credit: H. Zell (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Madame Pele Breezes Back In

This post first appeared on Patreon. To support this site and gain early access to select posts, plus behind the scenes, sneak peeks, and exclusive content, become a patron today.
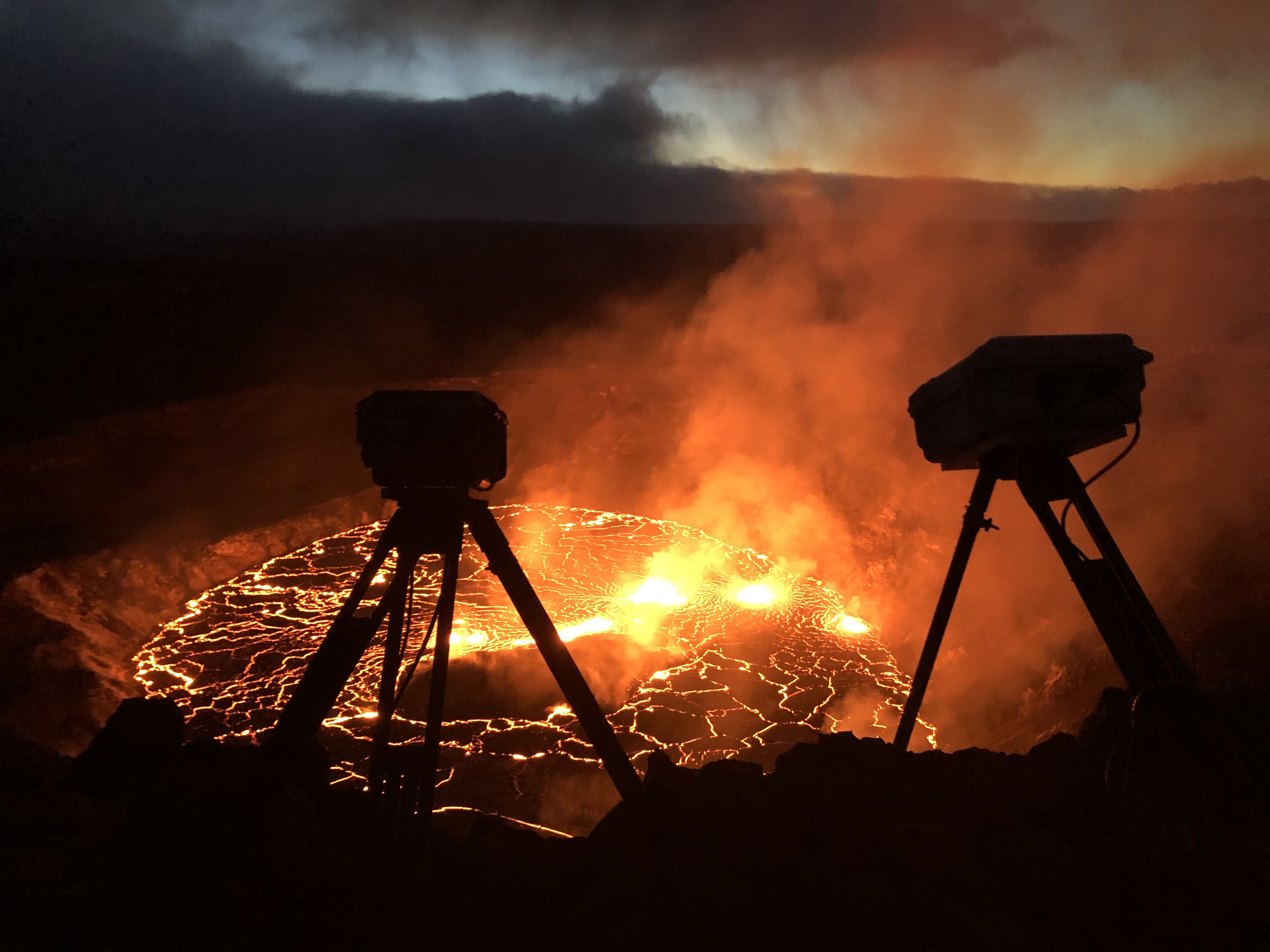
Allow me to set the scene: bugger-all was going on at Kilauea Volcano. Madame Pele had shut up shop in May and taken a luana iki (little rest). Perhaps she paid a visit to Iceland’s bouncing baby shield volcano. She may have stopped by La Palma to give her cousin some encouragement.
Back at Kilauea, there were a few rumbles in late August, with an intrusion of magma to the summit. But after that delivery, nothing much happened for most of September. It seemed to many that Pele’s luana iki might turn in to a long winter’s nap.
Madame had no such plans.

Timelapse showing the onset of the eruption. Watch the lower right tip of the island at the beginning – that frame is looped so you can see the uplift right before the vent opens. Click here for a full-size image. Credit: USGS
The Lowdown on LAZE: La Palma Eruption’s Most Recent Hazard
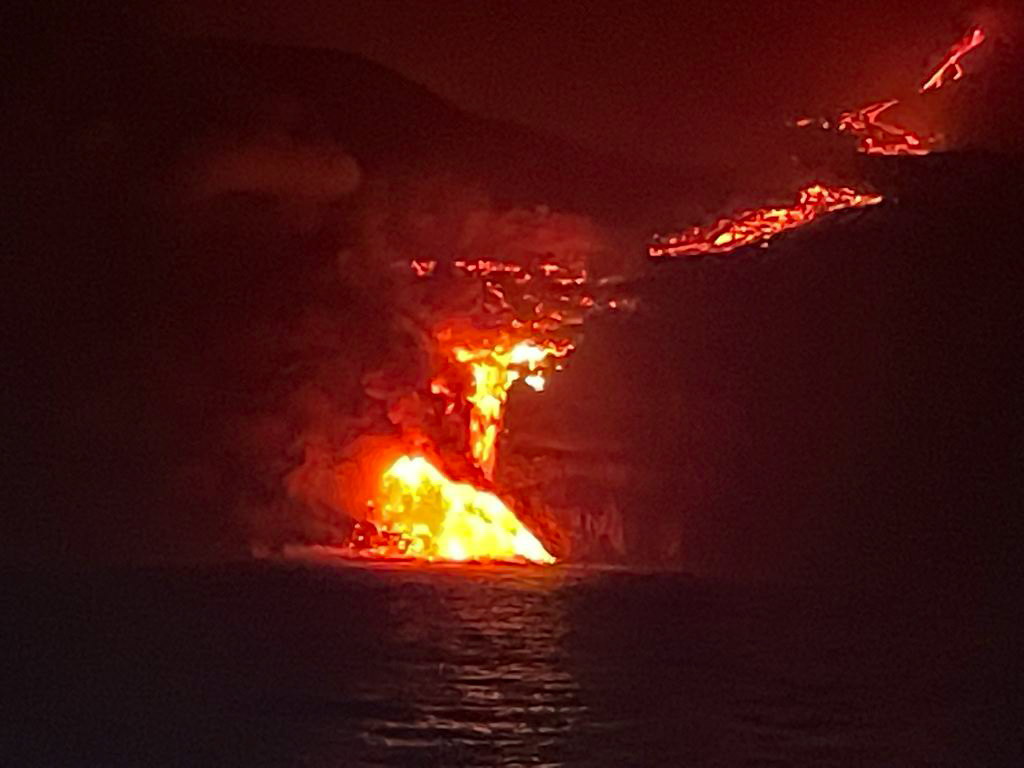

The lava flow from La Palma’s ongoing eruption has reached the Atlantic Ocean. The news is full of people talking about how hazardous this is: you can get all kinds of explosive interactions between water and molten rock. There’s also the little matter of LAZE. Now seems like the perfect time to bring you this article, first published at Scientific American Blogs, telling you what to expect from those dense white plumes.
And I’d also like to take this opportunity to remind you why it’s a terribad idea to sail too close to an ocean entry. Keep your distance!
Kilauea’s most recent lava flows reached the sea over the weekend, and they’ve been beach bumming ever since. Few things are as dramatic as molten rock contending with seawater. We’ll be talking about all the neato things that are happening and that we may see if the eruption continues. We’re starting with LAZE, which in this case isn’t something you do on a hot summer afternoon. It’s this:

A dense LAZE plume rises from the Pacific Ocean during Kilauea’s 2018 eruption. Credit: U.S. Geological Survey
When blazing hot lava meets seawater, the interaction between them boils the water and produces enormous plume of mist, called LAZE (lava haze). These plumes are, of course, mostly water vapor, but they are so much more than that. They’re acidic beasts carrying appreciable amounts of hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, sulfate anion, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide, plus traces of volcanic glass and other particles. Even if you could find a safe place near where the lava is pouring into the ocean, you wouldn’t want to be hanging out there without industrial-grade protection.
Sounds super scary, right? Well, it’s concerning. But don’t panic. It, like so many of Kilauea’s other dangers, is something you can protect yourself against with a little common sense and caution. And it’s really pretty neat. (more…)
La Palma Eruption: Video Updates
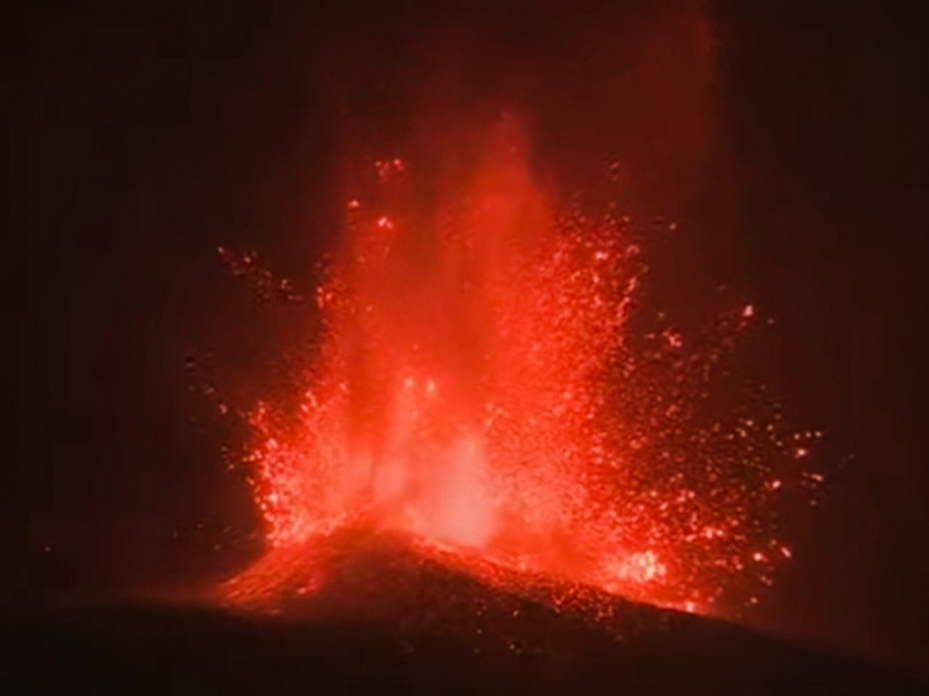

I’m cooking up a great series of posts for you on the geologic context of La Palma, the seismic signs of this eruption, and the eruption itself, plus human efforts to control lava flows. But I had to pause to show you this wonderful trio of videos from Geology Hub, which not only include information on the ongoing eruption, but have some incredible clips. Plus, a Canary Islands bonus volcano!
Here’s an update from a couple of days ago, while new fissures were opening and the volcano was still in a largely Hawaiian-type eruptive style.
Many people seem to love to jump on the slightest easing of eruptive activity to declare that the eruption is obviously not going to last for a long time and it’s just about to end. Those people get heartily laughed at by eruptions, which frequently wax and wane and wax again many times through the course of an eruption that will last weeks, months, or years. The new La Palma volcano is certainly having a good snicker as it shifts to Stombolian activity and increases in vigor. Personally, I think it’s going to be with us for months, if not years.
Watch closely, and you’ll see an urban kipuka in one of the shots. I’m so glad these flows are slow enough for people to get to safety before their homes and towns are destroyed. And so far, it seems that Canary Islands officials have been doing a good job listening to what the volcano is telling them and ensuring folks can get out of harm’s way. (more…)
